Automate #1: Spotify Podcast Mirror
How I created an Automator application, which records the latest episode of a Spotify podcast, fills out metadata and generates a file for metadata for a podcast client to subscribe to. · Frankfurt, GermanyThis is the first post of my series Automate.
In this post I describe how I created an Automator application, which will record the latest episode of a Spotify podcast, fill out metadata like title and description and generate a file for metadata for a podcast client to subscribe to.
Preparation
If you want to follow along, you need a machine with macOS and the following installed:
- Spotify
- Audio Hijack ($77, sorry)
- jq
- Golang
You also need a bit of knowledge in Apple Script, Bash scripting and JSON and be comfortable in a terminal.
Create Audio Hijack Session
Audio Hijack is an application that can do complex audio pipelines, often used for recording podcasts or live streaming. We use this to capture the output of Spotify to a file. Audio Hijack has a concept of sessions, meaning various saved pipelines.
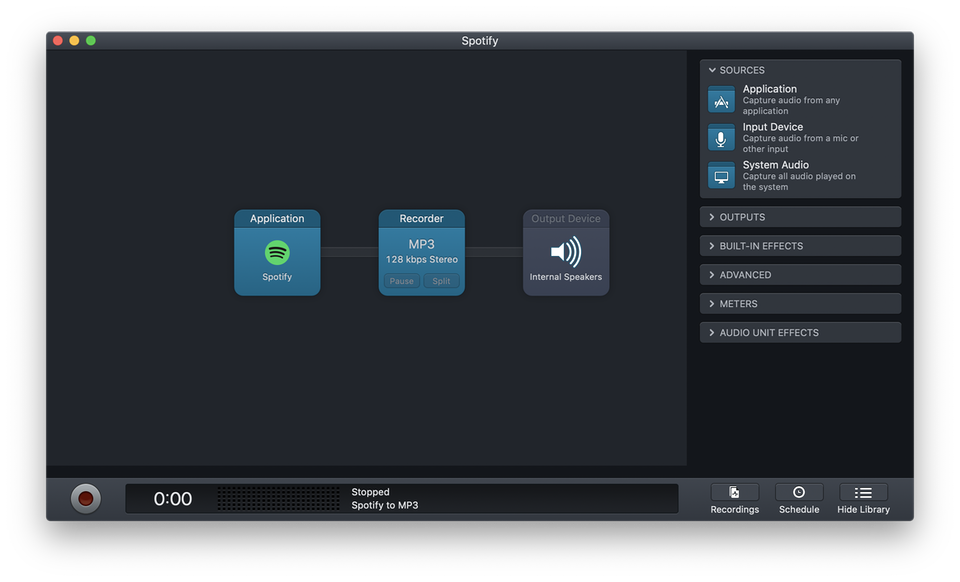
To prepare things, start Audio Hijack and create a new session based on the Application Audio template.
This post assumes you only have on session. If you have multiple, make sure it’s at the first position. In the session, select Spotify as Application and change the Recorder to 128 kbps (or whatever you prefer). I recommend disabling the Output Device, but it’s helpful if you want to debug something. After saving, it should look similar to this:
Spotify Credentials
We need various metadata about the latest show, like title, Spotify uri or duration.
To get those, we use the Spotify Web API. You need to create a Spotify App by going to the developer dashboard and create a client id.
Fill out the fields and you’ll get a Client ID and a Client Secret.
Spotify ID
We also need the Spotify ID of the podcast you want to mirror. To get that, click the three dots on the podcast page in Spotify, select Share and Copy Spotify URI.
The uri looks something like spotify:show:abcdef, where abcdef is your Spotify ID.
Folder Setup
Lastly, there needs to be a folder where the podcast lives. We use a tool in our last step to generate the RSS feed, so we can subscribe to the podcast from our favourite podcast app. Fot the tool to work, we need to have a podcast.toml similar to this example, but without the [[episodes]] parts in our folder.
There also needs to be an empty subfolder called dist/.
Let’s do this
1. Create an Automator Project
Open the Automator app and choose New Document.
Then click on Application to build a .app file you can launch later.
2. Get Latest Episode Metadata
We need the following attributes of the latest episode:
- Spotify URI
- Duration
- Name
- Description
- Release date
We use Bash to get the data, so drag a new Run Shell Script onto your workflow with the following contents:
#!/bin/bash
# Exit the script if any command returns an error code.
# Define variables
PODCAST_PATH='/path/to/podcast/folder'
SPOTIFY_ID='abcdef'
AUTH_HEADER='abcdef123456' # base64 encoded `<client id>:<client secret>`
# Get Spotify access token
TOKEN_RES=
ACCESS_TOKEN=
# Get show
SHOW_RES=
# Get first (latest) item
ITEM=
# Get release date
RELEASE_DATE=
# If the episode already exists, exit early
if [; then
()
fi
# Get and echo metadata, each line will be a parameter to the next action
# in the Automator workflow.
|
|
|
|
We need the metadata again later, so save it in a variable by dragging the Set value of variable below the Bash action and giving it a name (e.g. Metadata).
3. Start the Recording Process
Now we get to the messy part. Drag a Run AppleScript action to the end of the workflow and paste the following code.
Read the comments (lines starting with --) to know what it’s doing. Make sure the checkbox next to Automator in System Settings → Security & Privacy → Accessibility) is checked, otherwise you will get an error and the keyboard shortcuts won’t work.
on run
-- Prepare Spotify
-- Start recording
-- Play track
end run
4. Save Release Date to it’s Own Variable
We use the publish date of the episode as filename, so we need to get this first. Drag the action Get Value of Variable into your workflow and select the Metadata variable (or whatever you called it). After that, drag a Run AppleScript action at the end with the following contents.
on run
-- Return the fifth parameter of our Metadata variable,
-- which is the release date
return item 5 of input
end run
Set the variable ReleaseDate using a Set Value of Variable action.
5. Move File to Destination
Use a Find Finder items action to search the destination folder of your Audio Hijack session for files with all of the following attributes:
- Kind is music
- Date created is today
Then drag a Run AppleScript with the following contents into your workflow to get the first item (which will be the latest).
on run
# Get latest item
return item 1 of input
end run
After that, rename the file using Rename Finder Items. Choose Name Single Item and set Basename only to ReleaseDate.
Then move the renamed file to podcast-folder/dist/episodes/ with a Move Finder Items action.
6. Metadata and Deployment
Now that we have our recording, we have to generate the RSS feed with the metadata so podcast clients can display the episodes in a nice list. After that we upload both the feed and the episode.
Use Get Value of Variable to get the Metadata variable again.
To generate the feed.xml, we append the metadata of an episode to a simple TOML file. I wrote a small tool for this, which you can find here: toml-podcast.
After generating the feed.xml, we use the AWS CLI deploy it and the newly recorded episode to an AWS S3 bucket.
Add a Run Shell Script action with the following contents:
#!/bin/bash
PODCAST_PATH='/path/to/podcast/folder'
URI=""
DURATION_MS=""
TITLE=""
# For description, we have to escape double quotes ("), because the TOML strings
# use double quotes as well.
# If the TOML is invalid, toml-podcast will crash.
DESCRIPTION=
RELEASE_DATE=""
# Add episode metadat to the end to podcast.toml
# Build feed.xml using toml-pdocast
# Your $GOBIN will look different, find out your path by typing `which toml-podcast`
# in your terminal
# Set AWS credentials (replace with your real credentials)
# Upload episodes + feed.xml
I use a Cache-Control header because I serve the podcast via a CloudFront, the AWS CDN and I want the feed.xml to be at most 10 minutes old.
Conclusion
Now recording the latest episode of your favourite Spotify podcast takes one click. If you have a spare Mac you could even start it automatically matching the release cycle of the podcast.